Renewable Energy Development in Germany
Energiewende
Germany is committed to transitioning towards a sustainable energy system through its Energiewende policy. The goal is to phase out nuclear power and reduce greenhouse gas emissions by adopting renewable energy sources.
Renewable Energy Act (EEG)
The Renewable Energy Act (EEG) was implemented in 2000 to promote renewable energy generation in Germany. It introduced feed-in tariffs that guarantee fixed payments to renewable energy producers, encouraging their development.
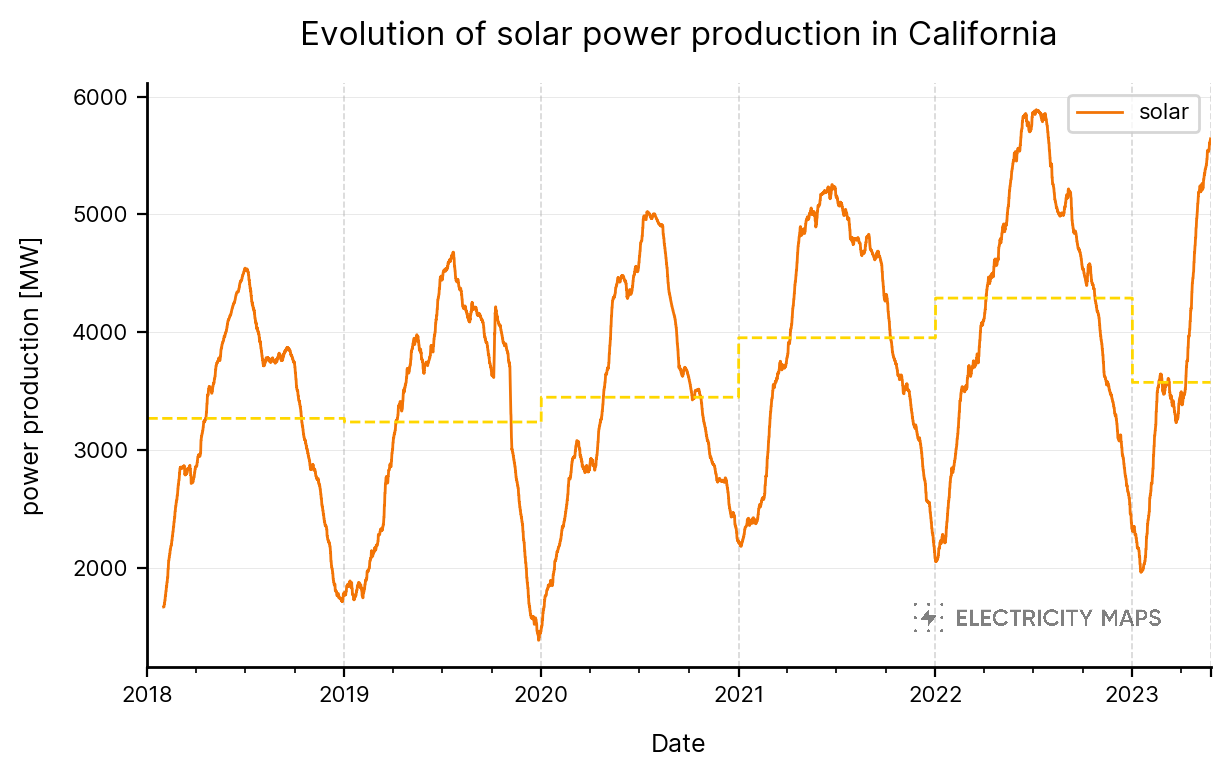
As of 2020, renewables accounted for over 50% of Germany's electricity consumption, with wind and solar power contributing the most. The government aims to achieve a target of at least 65% renewable energy by 2030 and a carbon-neutral economy by 2050.
Solar Production in California
Solar Energy in California
California is a leader in solar energy production and has been at the forefront of solar power development in the United States.
Solar Installations
California has a significant number of solar installations, including both residential and commercial systems.
Large-Scale Solar Power Plants
California is home to numerous large-scale solar power plants that contribute to the state's renewable energy goals. These plants utilize photovoltaic (PV) technology to convert sunlight into electricity.
Solar Energy Capacity
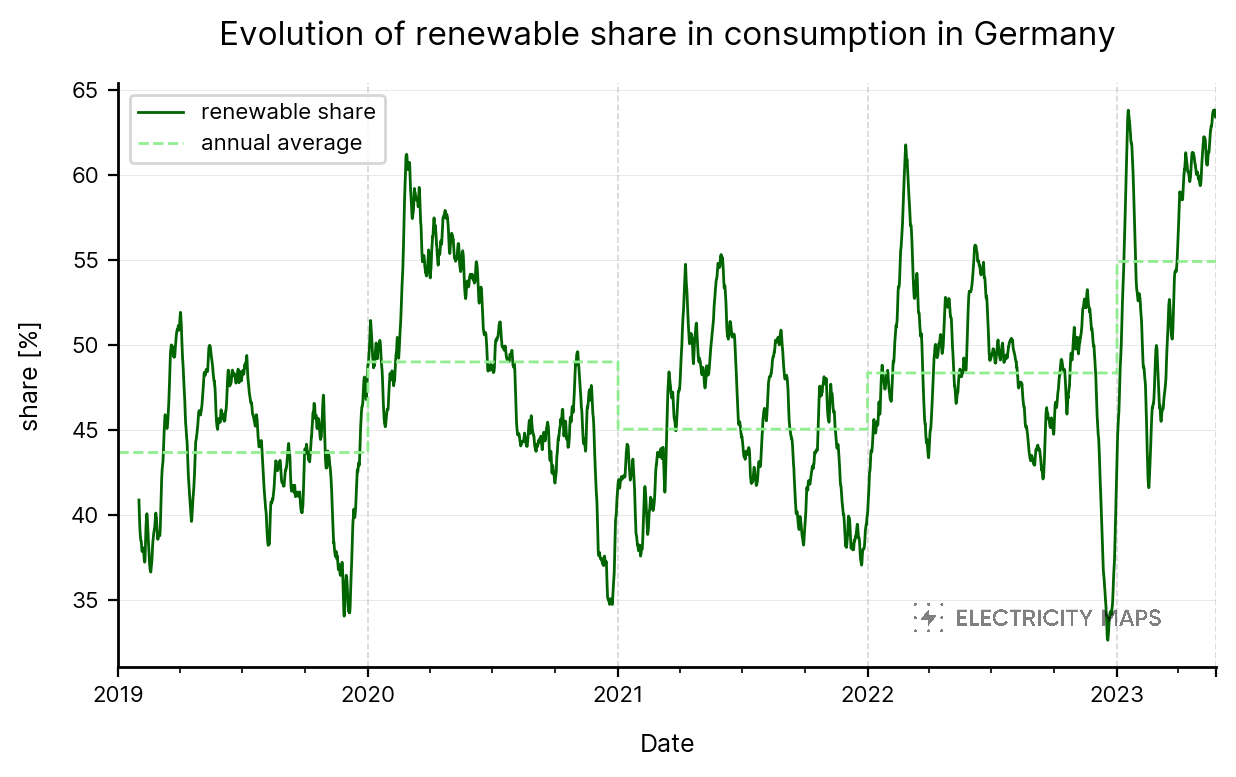
As of 2023, California had a total solar capacity of 17947.7 megawatts (MW), making it one of the largest solar markets in the world.
Solar Incentives
California offers various incentives to promote solar energy adoption, including state and federal tax credits, rebates, and financing programs.
Environmental Benefits
Solar energy helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions and dependence on fossil fuels, contributing to California's efforts to combat climate change and promote a cleaner and more sustainable energy system.
California's commitment to solar energy has played a crucial role in the state's renewable energy transition, fostering economic growth, job creation, and environmental sustainability.